Difference between revisions of "ThunderGuppy"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
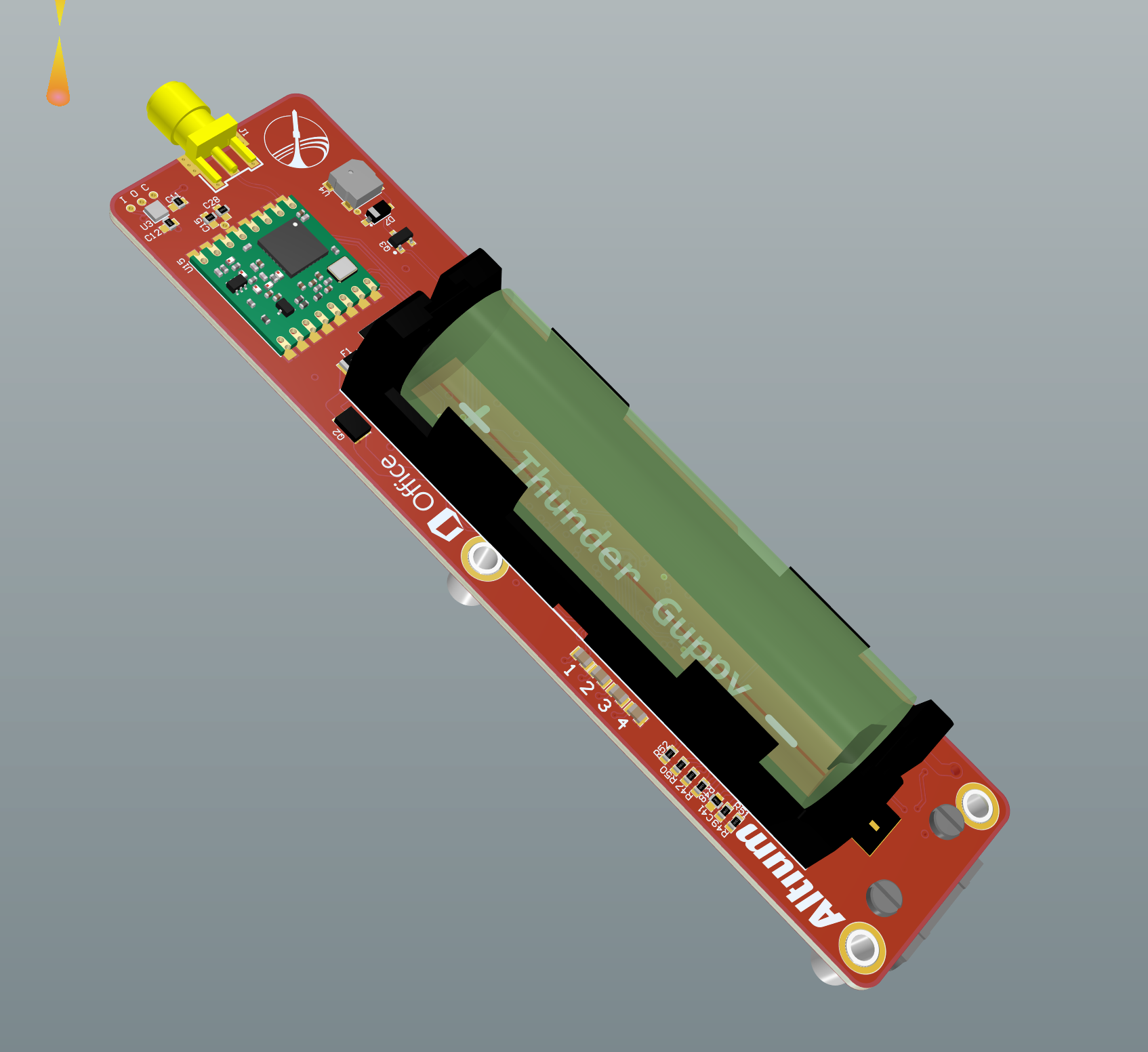
ThunderGuppy is the third generation of SSI rocket flight computer. It's hardware was developed in 2019 by Tim Vrakas. ThunderGuppy followed the SkyBass and SpaceSalmon, making the naming scheme O-Fish-ial. ThunderGuppy was the smallest generation of the family to date, and was designed to fit as a standalone module into a standard 2" airframe, much like the Stratrologger and Raven COTS Altimeters. | ThunderGuppy is the third generation of SSI rocket flight computer. It's hardware was developed in 2019 by Tim Vrakas. ThunderGuppy followed the SkyBass and SpaceSalmon, making the naming scheme O-Fish-ial. ThunderGuppy was the smallest generation of the family to date, and was designed to fit as a standalone module into a standard 2" airframe, much like the Stratrologger and Raven COTS Altimeters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Guppy_Front.png|frame|caption]] | ||
=== Hardware Features === | === Hardware Features === | ||
Revision as of 03:40, 19 July 2020
ThunderGuppy is the third generation of SSI rocket flight computer. It's hardware was developed in 2019 by Tim Vrakas. ThunderGuppy followed the SkyBass and SpaceSalmon, making the naming scheme O-Fish-ial. ThunderGuppy was the smallest generation of the family to date, and was designed to fit as a standalone module into a standard 2" airframe, much like the Stratrologger and Raven COTS Altimeters.
Hardware Features
From the start, ThunderGuppy was designed to be mostly compatible with the earlier SpaceSalmon. Aside from the major change to form factor, Guppy introduced the following changes:
- Integrated S6C and GPS hardware, in place of an add-on RF carrier module needed for SpaceSalmon.
- Two FET-based squib drivers, in place of the MC33797 4-channel squib driver IC. These are not designed to safely control high-risk initiators, but decrease complexity.
- A single 18650 Li-Ion cell. This was needed to satisfy the form factor requirement.
- Dual accelerometer banks, each with high and low range 3-axis sensors. This allows emulation of a high-range gyroscope by indirect measurement of centripetal acceleration.